The core role of a thermal energy supplier is to provide industrial users with "customized, stable, and efficient" thermal energy solutions rather than simply "selling thermal energy". Its service logic centers on "users’ thermal energy needs", with key responsibilities including:
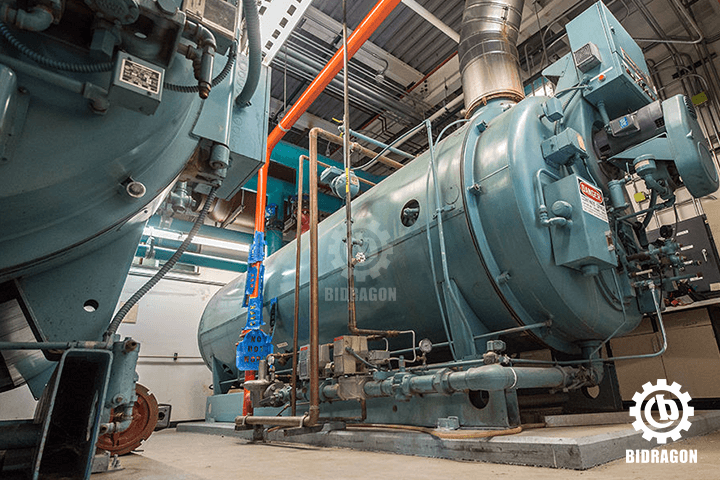
A thermal oil boiler is an industrial boiler that uses thermal oil as the heat carrier. It heats the thermal oil through combustion or electric heating, then transports the high-temperature thermal oil to the user’s thermal equipment (e.g., reaction kettles, dryers) via a circulating pump to achieve "indirect heat transfer". It becomes one of the preferred equipment for thermal energy suppliers due to its core advantages:
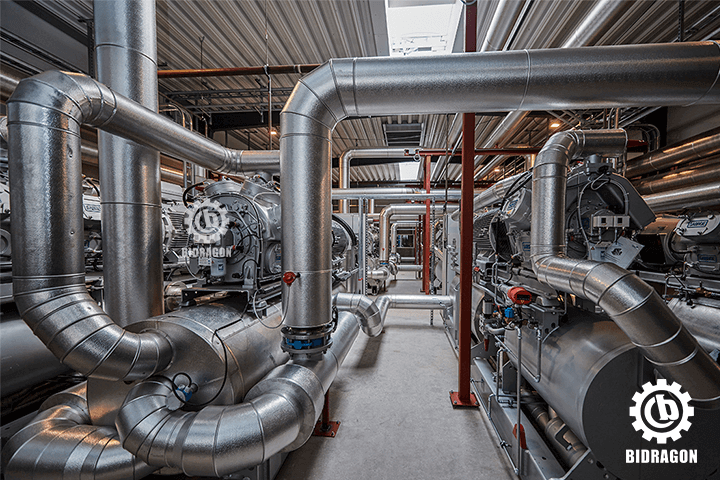
Choose a heater with a simple structure, easy maintenance, and readily available spare parts. In addition, ensure that the supplier provides strong technical support and after-sales service, as this will minimize downtime and ensure long-term stable operation.