The industrial boiler system is a complex whole with many components that work together in a precise manner. Its operation involves the transmission and conversion of multiple media such as water, steam, and fuel. Any error in any link may affect the stability and safety of the entire system. In such a complex system, valves play a core and irreplaceable role, and can be called the "nerve center" and "control hub" of the system.
The valve can effectively control the flow of the medium through precise opening, closing, and opening adjustment to ensure that the heating surfaces, pipes and other components of the boiler are supplied with an appropriate amount of medium; at the same time, it can adjust the temperature in the system to keep the boiler within the optimal combustion and heat exchange temperature range; in addition, the regulation of pressure is an important responsibility of the valve, maintaining the system pressure in a reasonable range and preventing dangerous situations such as overpressure. It can be said that valves are key components to ensure the safe, efficient and stable operation of industrial boilers, and the quality of their performance is directly related to the overall performance of the boiler system.
In industrial boiler systems, the functions of valves are diverse and crucial, which are specifically reflected in the following aspects:
Controlling flow and pressure is the most basic and core function of valves. When the boiler is running, it is necessary to accurately control the flow of water, fuel, steam and other media entering the boiler according to different working conditions to ensure combustion efficiency and heat exchange effect. At the same time, the pressure in the system must be maintained within the specified range. Too high pressure may cause serious safety accidents such as boiler explosion, and too low pressure will affect the output of the boiler. The valve ensures that the flow and pressure are always at a reasonable level through its own regulation. Preventing overpressure and equipment damage is a key function of the valve to ensure system safety. When an abnormal situation occurs in the system and the pressure exceeds the set value, specific valves such as safety valves will automatically open to discharge excess media and reduce system pressure, thereby avoiding damage to the boiler and other equipment due to overpressure and protecting equipment and personnel safety. Provide isolation function for easy inspection and maintenance. When the boiler system needs to be inspected, parts replaced or maintained, the valve can isolate the part to be inspected from other parts of the system, prevent the flow of media, enable the inspection work to be carried out safely and smoothly, reduce downtime, and improve the maintainability of the system. Ensure efficient and safe operation of the system. Appropriate valves can reduce the energy loss of the medium during transmission, improve the thermal energy utilization efficiency of the system, and reduce energy consumption. At the same time, its stable and reliable working state is an important guarantee for the safe operation of the system, avoiding various safety hazards caused by valve failure.
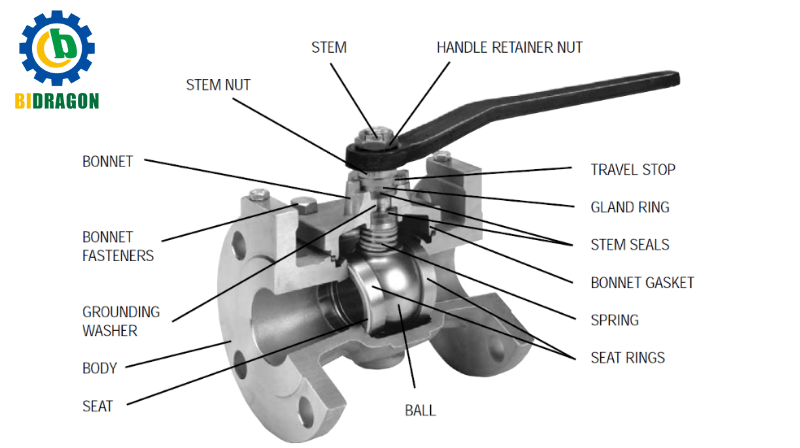
Structure and working principle: The ball valve is mainly composed of valve body, ball, valve stem and sealing ring. There is a circular through hole on the ball, which drives the ball to rotate through the rotation of the valve stem. When the through hole is consistent with the pipeline axis, the valve is fully open and the medium can pass smoothly; when the ball rotates 90 degrees and the through hole is perpendicular to the pipeline axis, the valve is fully closed to block the flow of the medium.
Applicable scenarios: In industrial boiler systems, it is often used in steam supply lines and other occasions that require rapid closure. It can quickly cut off the flow of the medium and has a fast response speed.
Advantages and disadvantages analysis: The advantages are good high pressure and high temperature resistance, suitable for working in the high pressure and temperature environment of industrial boilers; good sealing performance, small leakage; compact structure and easy operation. The disadvantage is that it is not suitable for flow regulation, because the structural characteristics of the sphere determine that the flow changes greatly during the regulation process, making it difficult to achieve precise flow control.
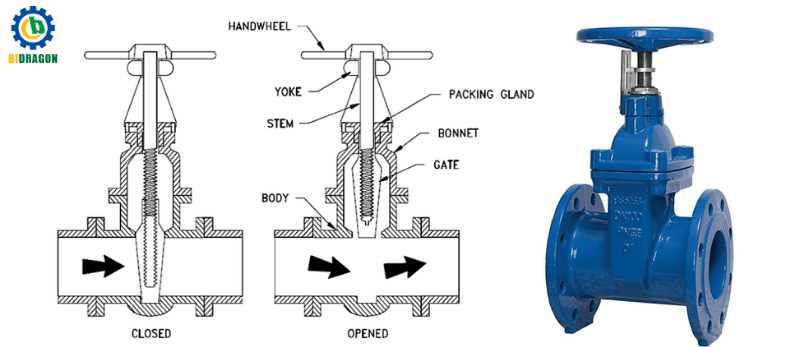
Structure and working principle: The gate valve consists of a valve body, a gate, a valve stem, a valve cover and other components. The gate moves up and down in a direction perpendicular to the axis of the pipeline, and the opening and closing of the valve are controlled by the lifting and lowering of the gate. When the gate is fully lifted, the valve is fully open, and the channel through which the medium passes is straight-through with less resistance; when the gate is lowered to the closed position, the flow of the medium is blocked.
Applicable scenarios: Suitable for large-flow steam or water supply systems, and widely used in large-flow occasions such as the main water supply pipeline and main steam pipeline of industrial boilers.
Advantages and disadvantages analysis: The advantages are small fluid resistance, low pressure loss when the medium passes, and can reduce the energy loss of the system; suitable for full-open and full-close operation, with good sealing performance. The disadvantage is that it is not suitable for flow regulation, because when the gate is partially opened, a large pressure difference will be generated on both sides, which is easy to cause erosion and wear on the gate and valve seat; and the structure of the gate valve is relatively complex, and it takes a long time to open and close.
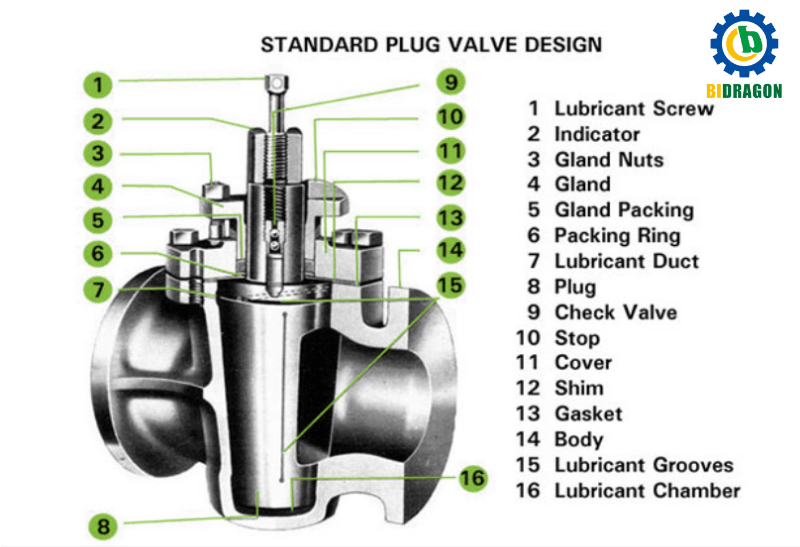
Structure and working principle: The plug valve is mainly composed of a valve body, a plug, a valve stem and a drive device. The plug moves horizontally in the valve body, and the valve is closed and opened by inserting or withdrawing the plug. A tight seal is used between the plug and the valve seat to ensure the sealing when closed.
Applicable scenarios: As a fast switching valve, it is often used in high-pressure systems and is used in some high-pressure auxiliary pipelines of industrial boilers, such as branch pipelines of high-pressure steam.
Advantages and disadvantages analysis: The advantage is fast operation, and the valve can be fully opened or fully closed in a short time; the structure is simple and easy to maintain. The disadvantage is that there is a high operating torque requirement, and a large driving force is required to realize the movement of the plug; although it can be used for a small amount of flow control, the control accuracy is low and it is not suitable for precise flow regulation.
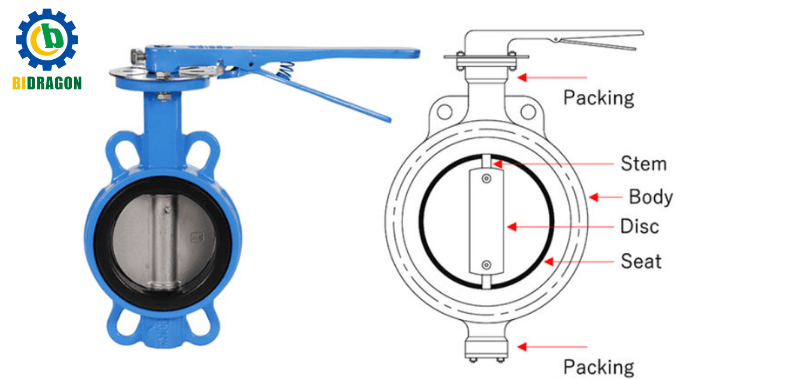
Structure and working principle: The butterfly valve consists of a valve body, a butterfly plate, a valve stem and a drive device. The butterfly plate is installed on the shaft in the valve body, and the rotation of the valve stem drives the butterfly plate to rotate within a range of 90 degrees, thereby controlling the opening and closing of the valve. When the butterfly plate is parallel to the pipeline axis, the valve is fully open; when the butterfly plate rotates 90 degrees and is perpendicular to the pipeline axis, the valve is fully closed.
Applicable scenarios: It is suitable for compact boiler systems and is a low-cost option. It is more common in some industrial boiler auxiliary systems that do not require high control accuracy and have limited space.
Advantages and disadvantages analysis: The advantages are simple structure, small size, light weight, and small installation space requirements; low cost and good economy; flexible operation and fast switching. The disadvantages are poor flow regulation effect and difficulty in achieving precise flow control; in high-pressure and high-temperature environments, its sealing performance and service life will be greatly affected, because high temperature and high pressure will accelerate the aging and wear of seals.
Structure and working principle: The globe valve consists of a valve body, a valve disc, a valve seat, a valve stem and other components. The valve seat and the valve body form a channel, and the valve disc changes the gap between the valve seat and the valve seat by lifting the valve stem, thereby controlling the flow of the medium. When the valve disc rises, the gap increases and the flow increases; when the valve disc drops to close contact with the valve seat, the valve closes and blocks the flow of the medium.
Applicable scenarios: It is suitable for precise flow regulation, especially in high temperature and high pressure environments. It is widely used in industrial boilers, such as the cooling and pressure reduction system and steam distribution system, where precise flow control is required.
Advantages and disadvantages analysis: The advantage is that it can provide precise flow control, good regulation performance, and can achieve smooth flow regulation in a large range; the sealing performance is reliable. The disadvantage is that the medium needs to change the flow direction when passing through the valve, which will cause a large pressure loss and increase the energy consumption of the system; and because the valve disc needs to overcome the pressure of the medium during the lifting process, it requires a large operating force.
Working pressure and temperature conditions are important bases for selecting valves. Different types of valves have their specific pressure and temperature application ranges. In industrial boiler systems, it is necessary to select appropriate valves based on the actual working pressure and temperature of the system. For example, for high-pressure and high-temperature main steam pipelines, ball valves and globe valves that can withstand the corresponding high pressure and high temperature should be selected; while for auxiliary pipelines with lower pressure and temperature, butterfly valves may be more economical choices.
System flow requirements and control accuracy are also crucial. If the system requires precise flow regulation, such as a temperature reduction and pressure reduction system, a globe valve is a better choice; if only full opening and closing operations are required, gate valves can be selected for large flow occasions, and ball valves or gate valves can be selected for fast switching occasions.
Safety and maintenance convenience cannot be ignored. The safety performance of the valve is directly related to the safe operation of the boiler system. Valves with reliable safety guarantees should be selected, such as safety valves that must comply with relevant safety standards. At the same time, the convenience of valve maintenance should be considered. Valves with simple structures and easy disassembly and replacement of parts can reduce maintenance time and costs.
Operation response time and applicability also need to be considered. In situations where a quick response is required, such as emergency cut-off of steam supply lines, ball valves, gate valves and other fast-responding valves are more suitable; while for situations with low operating frequency and low response time requirements, gate valves may be more suitable.
In the energy industry, such as the industrial boiler system of a thermal power plant, the main steam pipeline has high pressure, high temperature and large flow. Gate valves are usually selected as isolation valves, globe valves are used for flow regulation, and safety valves are used as safety devices. This is because the energy industry has extremely high requirements for system stability and safety, and these valves can meet its needs for high pressure, high temperature, large flow and precise control.
Industrial boiler systems in the chemical industry often involve corrosive media. When selecting valves, the corrosion resistance of the valves needs to be considered. For some highly corrosive pipelines, ball valves or globe valves made of special materials may be selected to resist the corrosion of the medium and ensure the service life and sealing performance of the valve.
Industrial boiler systems in the food processing industry have high requirements for hygiene, and the structure of the valve should be easy to clean to avoid medium residue. In the steam supply and hot water circulation system, stainless steel ball valves or butterfly valves may be selected. These valves have relatively simple structures, are easy to clean, and can meet the hygiene standards of the food processing industry.
Leakage is one of the common problems of boiler valves, which may be caused by wear, aging, improper installation of seals, etc. Leakage not only leads to waste of medium, but also causes heat loss, reduces the thermal efficiency of the boiler, and the leaked medium may cause damage to surrounding equipment and the environment.
Corrosion and wear are also common problems. The medium in the industrial boiler system may contain corrosive components, or the medium may cause erosion and wear to the internal parts of the valve when flowing at high speed. After long-term use, the sealing performance of the valve will be reduced and the structure will be damaged, affecting the normal operation of the valve.
Valve failure will lead to reduced boiler efficiency and safety hazards. After the valve fails, the flow, pressure and other parameters cannot be controlled normally, which will make the operation state of the boiler system unstable, reduce thermal efficiency, and increase energy consumption; in severe cases, it may cause safety accidents such as system overpressure and pipe burst, endangering the safety of personnel and equipment.
Identifying valve problems can be done through daily observation and testing, such as checking whether the valve has signs of leakage, whether there is any abnormal sound during operation, whether the valve opens and closes smoothly, etc. Regularly performing pressure tests and sealing tests on the valve can also detect potential problems in a timely manner.
To prevent valve problems, first of all, you should choose valves with reliable quality and suitable for the system conditions; secondly, you should do a good job of water quality treatment in the system, reduce the corrosive components and impurities in the medium, and reduce the corrosion and wear of the valve; at the same time, operate the valve reasonably to avoid damage to the valve caused by excessive or improper operation.
Regular inspection and cleaning are essential. A regular inspection plan should be formulated to check the appearance, operating performance, and sealing performance of the valve; for valves that are prone to deposits, such as steam valves, they should be cleaned regularly to remove internal mineral deposits and impurities to ensure the smooth flow and sealing performance of the valve.
Replace damaged seals in time. Seals are key components to ensure the sealing performance of valves. Once the seals are found to be worn, aged or damaged, they should be replaced in time to prevent leakage.
Select appropriate materials and valve designs to reduce corrosion and wear. According to the nature, pressure, temperature and other conditions of the system medium, choose valves made of corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant materials, such as stainless steel in corrosive media and streamlined valves in high-speed flow media to increase the service life of the valve.
The installation position and alignment of the valve are crucial. Make sure that the valve is installed in the correct position and meets the process flow and operation requirements of the system. For example, the safety valve should be installed at the highest position of the boiler or in a part prone to overpressure. The valve and pipeline flow direction must be aligned to avoid increased medium flow resistance, increased valve wear or decreased sealing performance due to installation misalignment. Fix it with bolts or welding during installation to ensure that the valve will not move or vibrate during operation.
There are requirements for threaded and flange installation. For threaded valves, the valve needs to be screwed into the pipeline. Before screwing in, apply suitable sealing materials, such as sealing tape or sealant, on the threads to ensure sealing performance. Pay attention to moderate force when screwing in to avoid excessive tightening and damage to the threads. Flange valves require gaskets to ensure sealing. The material of the gasket should be selected according to the system's medium, pressure and temperature. During installation, the flange surface should be flat and clean, and the bolts should be tightened evenly to avoid leakage due to uneven force.
Cleaning method: First disassemble the valve and break it down into its components; then soak the components in descaling liquid or vinegar to remove mineral deposits; after soaking for a period of time, use a brush to scrub the dirt on the surface of the components, and then rinse with clean water to remove the residual descaling liquid or vinegar; finally, dry the components to ensure that there is no residual moisture before reassembling the valve.
Repair process: First close the system where the valve is located and release the pressure in the system; then disassemble the valve and check whether the sealing ring or gasket is damaged. If damaged, replace it in time; clean the valve seat, remove the dirt and impurities on the valve seat, and ensure that the valve seat surface is flat; check the valve stem to ensure that the valve stem can move freely. If there is a stuck phenomenon, add an appropriate amount of lubricant or perform appropriate grinding treatment; finally reassemble the valve and perform a sealing performance test.
The size selection of the pressure safety valve should be based on the maximum steam flow and set pressure of the system to calculate the required pressure discharge capacity. The calculation formula is usually based on parameters such as steam flow, pressure and valve discharge coefficient to ensure that the valve can discharge enough steam in time when the system is overpressured, so that the system pressure can be quickly reduced to a safe range to avoid damage to the system due to overpressure.
Ensure efficient operation: The valve accurately controls the flow of water and steam so that each heating surface of the boiler can obtain an appropriate amount of medium, ensuring that the heat generated by fuel combustion can be fully absorbed and utilized, and improving the thermal energy utilization efficiency of the system. Reasonable valve configuration can reduce the resistance and leakage of the medium during transmission, reduce energy loss, and thus improve the overall operating efficiency of the boiler.
Safety protection: Valves are crucial in ensuring the safety of the boiler system. The safety valve can automatically open when the system pressure exceeds the set value to release excess media, preventing serious equipment damage accidents such as boiler explosions due to overpressure; stop valves, gate valves, etc. can quickly cut off the medium supply in an emergency to avoid the expansion of accidents; the stable operation of other types of valves can also prevent safety hazards caused by medium leakage, abnormal flow, etc.
Adapt to pressure and temperature: The selected valve must match the pressure, temperature and material requirements of the system. Different valve materials and structures can withstand different pressure and temperature ranges. If inappropriate valves are used, valve deformation and sealing failure may occur at higher pressures or temperatures, resulting in performance degradation and even safety accidents.
Water quality and corrosion protection: The water quality of the industrial boiler system has a great impact on the service life of the valve. Improper water treatment will cause impurities in the water to deposit inside the valve and form scale. At the same time, the corrosive components in the water will corrode the valve. Therefore, care should be taken to use valves that meet water quality requirements, select materials with good corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel, copper alloy, etc., and take appropriate water treatment measures to reduce valve corrosion and sediment accumulation.
Signs of valve damage
Valve leakage is a common sign of damage, which may be manifested as medium seepage at the valve connection or valve stem seal. Difficult operation is also an obvious sign, such as the valve feels heavy and stuck when opening or closing, and cannot be operated smoothly. In addition, the valve no longer accurately regulates the flow rate, and the flow rate fluctuates greatly, which is also a manifestation of valve damage.
The impact of valve failure on boiler performance
Leakage will lead to a decrease in thermal efficiency, because the leaking medium will take away a lot of heat, so that the boiler needs to consume more fuel to maintain normal operating parameters. Unstable steam pressure will affect the output and steam quality of the boiler, and have an adverse effect on the normal operation of steam-using equipment. At the same time, leakage and other failures may become safety hazards, such as steam leakage may cause scalding of personnel, and valve failure may cause system overpressure.
In summary, valves play an indispensable role in industrial boiler systems. Correctly selecting and maintaining boiler valves can not only ensure the efficient operation of the system, improve the efficiency of thermal energy utilization, and reduce energy consumption, but also extend the service life of the equipment, ensure the safe and stable operation of the system, and avoid the occurrence of various safety accidents. Therefore, in the design, installation, operation and maintenance of industrial boilers, we must pay full attention to the role of valves, reasonably select valve types according to actual working conditions, and strengthen daily maintenance and management to ensure the good operation of industrial boiler systems.