In solid fuel combustion systems, boiler grates play a vital role, which directly affects the combustion efficiency of fuel, the operation stability of boilers and the overall energy utilization effect. Without a suitable grate, solid fuel cannot be fully burned and the performance of the boiler will be greatly reduced.
A boiler grate is a component that supports solid fuels (such as biomass, coal, etc.) and enables them to burn. It is like a load-bearing platform that provides the necessary space and conditions for the combustion of fuel.
Its key components include the frame and grate plates, which are usually made of cast iron. This is because cast iron has excellent durability and heat resistance, and can work stably and long-term in high temperature environments.
The ventilation gap and air chamber are important structures of boiler grates. Air enters through the air chamber and then passes through the fuel layer through the ventilation gap on the grate, providing sufficient oxygen for combustion, thereby promoting the full combustion of fuel.
In terms of ash removal mechanism, there are manual and mechanical ash removal systems. Manual ash removal requires manual regular cleaning of the ash on the grate, which is suitable for small or simple boiler systems; while the mechanical ash removal system automatically completes the ash removal through mechanical devices, which improves the convenience and efficiency of operation and is suitable for large or highly automated boilers.
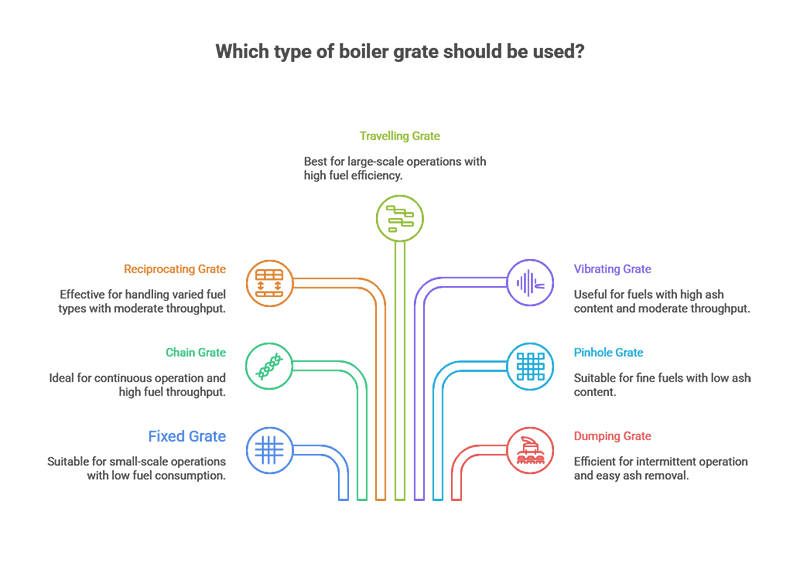
Different types of boiler grates differ in working principles, advantages and applicable fuel types, which will be introduced in detail below:
The fixed grate is simple in design and has no moving parts. Its structure is relatively simple and mainly consists of fixed grate pieces.
This grate is most suitable for low-moisture and low-volatility fuels. Because the combustion process of this type of fuel is relatively stable, complex grate movement is not required to assist combustion.
However, fixed grates require manual ash removal, and regular maintenance is required to ensure combustion efficiency and the service life of the grate.
The chain grate transports the fuel through the furnace through a constantly moving chain. The movement of the chain drives the fuel to gradually complete the combustion process in the furnace.
It is suitable for a variety of fuels, such as coal and biomass. Its high degree of automation can better control the combustion process, thereby improving combustion efficiency and the stability of boiler operation.
The reciprocating grate is designed for high-moisture and high-volatility fuels. It allows the fuel to be fully mixed and exposed to air through the reciprocating motion of the grate.
This grate can ensure uniform fuel distribution and smooth air circulation, which is conducive to the full combustion of the fuel, has high combustion efficiency, and is equipped with an automated ash removal device.
Travelling grates are designed for the efficient combustion of higher moisture fuels. They are widely used in biomass and multi-fuel boilers.
Characteristics:
Suitable for high moisture and high volatile fuels.
Provides even air distribution for efficient combustion.
Automated ash removal.
Higher cost but improved efficiency and automation.
The vibrating grate uses vibration to prevent slag formation and ash accumulation. Vibration keeps the fuel and ash moving, reducing their adhesion and agglomeration on the grate.
It is very suitable for biomass fuels that are prone to slagging, and can keep the grate clean and unobstructed, ensuring stable and strong combustion performance.
The pinhole grate has many small pores, which can provide uniform air distribution, thereby achieving uniform combustion of the fuel.
It is designed for biomass fuels with low ash content, but due to its narrow adaptability to fuels, its application range is limited and it is only suitable for specific scenarios.
The dumping grate can be tilted or tipped to discharge the ash and slag in the furnace. This design simplifies the ash removal process.
It is suitable for fibrous fuels, such as bagasse or agricultural waste, and can better handle the residues after the combustion of such fuels, improving the convenience and efficiency of fuel handling.
The boiler grate has many important functions in the combustion process. First, it supports the solid fuel layer so that the fuel can stay stably in the furnace for combustion.
Secondly, it provides a channel for air circulation, allowing air to pass through the fuel layer smoothly, providing sufficient oxygen for combustion, and helping the full combustion of fuel.
At the same time, it can ensure the complete combustion of fuel, maximize heat output, and reduce energy waste.
In addition, it can maintain the stability and rationality of the fuel placement in the furnace, providing a guarantee for the safe and efficient operation of the boiler.
Before the boiler grate is operated, a series of inspections are required to ensure its safe and stable operation:
Ensure that the boiler instruments (such as pressure gauges, water level gauges, valves, etc.) are working properly. These instruments are the key to monitoring the operating status of the boiler and can timely reflect important parameters such as the pressure and water level of the boiler.
Confirm that the water supply and water treatment systems are in good condition. Sufficient and qualified water quality is the basis for the normal operation of the boiler and can prevent scaling and corrosion inside the boiler.
Check the fuel supply system, including the storage, transportation, combustion and ignition devices of the fuel, to ensure that the fuel can be supplied continuously and stably, and the ignition device works reliably.
Check the blower, induced draft fan, damper and ventilation system to ensure that they operate smoothly. Good ventilation can provide sufficient oxygen for fuel combustion and discharge the smoke generated by combustion in time.
Common grate problems include the formation of slag and slag, which affects the combustion of fuel and the heat dissipation of the grate; mechanical wear or corrosion of the grate plates, which reduces the service life and performance of the grate; uneven combustion due to air leakage or misalignment, which reduces combustion efficiency and increases energy consumption.
Regularly clean and inspect the grate, remove ash and debris from the grate in time, and check whether the grate plates are damaged or worn; lubricate the moving parts to reduce friction between parts and improve their operational flexibility and service life; choose the right fuel and avoid using fuel that is prone to slag to reduce slag problems at the source; monitor the grate alignment and air flow distribution to ensure that the grate is operating properly and air can pass evenly through the fuel layer.
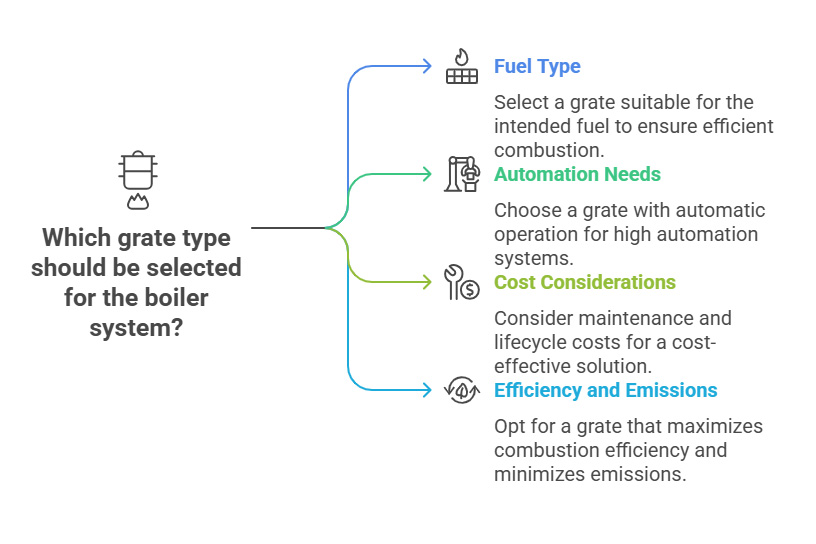
Choosing the right boiler grate requires considering multiple factors:
Different grates are suitable for different fuels. For example, fixed grates are suitable for low-moisture and low-volatile fuels; chain grates are suitable for a variety of fuels such as coal and biomass; vibrating grates are suitable for biomass fuels that are easy to slag, etc.
Boiler size and combustion load
The size and combustion load of the boiler determine the grate's carrying capacity and combustion area. It is necessary to select a grate size and type that matches the boiler to meet the combustion requirements.
If the boiler system has a high degree of automation, it is more appropriate to choose a grate with automatic operation functions (such as chain grates, reciprocating grates, etc.); if the number of operators is limited, the convenience of grate operation also needs to be considered.
Different types of grates have different maintenance costs and service lives. When choosing, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the initial investment, maintenance costs, and replacement costs, and choose a grate with high cost performance.
For scenarios with high requirements for combustion efficiency and emissions, it is necessary to select a grate type that can promote full combustion of fuel and reduce pollutant emissions.
The following is a comparison table of grate types and fuel types:
|
Grate Type |
Applicable Fuel Type |
|
Fixed Grate |
Low-moisture, low-volatility fuels |
|
Chain Grate |
Various fuels (coal, biomass, etc.) |
|
Reciprocating Grate |
High-moisture, high-volatility fuels |
|
Vibrating Grate |
Biomass fuels prone to slagging |
|
Pin-hole Grate |
Low-ash biomass fuels |
|
Dumping Grate |
Fibrous fuels (bagasse, agricultural waste, etc.) |
Boiler grate plays a key role in combustion efficiency, which directly affects the combustion completeness of fuel, the operation stability of boiler and energy utilization efficiency.
It is crucial to select the right grate according to the fuel type and system design. The right grate can maximize the performance of the boiler and reduce the operating cost.
At the same time, regular maintenance is encouraged, which can not only extend the service life of the boiler, but also optimize its operating performance and ensure the long-term, efficient and safe operation of the boiler.