The boiler feed pump is the core component of the industrial boiler system. Its core function is to extract the treated feed water from the water tank or deaerator, and deliver it to the boiler drum after pressurization, so as to provide the necessary water supply for the boiler to continuously generate steam. In the industrial production process, steam is an important power and heat source carrier. The stable operation of the boiler feed pump directly determines the output and quality of steam, which in turn affects the continuity and efficiency of the entire production system. Once the feed pump fails, the boiler will not be able to work normally due to lack of water, and may even cause safety accidents. Therefore, choosing the right type of boiler feed pump is not only related to the operating efficiency of the boiler system, but also a key link to ensure the safety and stability of industrial production.
The working process of the boiler feed pump can be simplified into three links: water absorption, pressurization and water delivery. First, the pump body introduces water from the water tank or deaerator into the pump through the suction pipe; then, the water is pressurized by the power generated by the impeller or volume change; finally, the pressurized water is delivered to the boiler through the output pipe. Throughout the process, the flow rate and head of the feed pump must accurately match the evaporation of the boiler. If the pump flow rate is too large, it will cause energy waste and system pressure fluctuations; if the flow rate is too small, it will not meet the water demand of the boiler, resulting in a decrease in steam production. Therefore, selecting an appropriate feed pump according to the actual evaporation of the boiler is an important prerequisite for ensuring the stable operation of the boiler.
The centrifugal pump throws out the water through the centrifugal force generated by the high-speed rotation of the impeller, converting mechanical energy into kinetic energy and pressure energy of the liquid. This type of pump has a simple structure and consists of main components such as the pump body, impeller, and pump shaft. During operation, the impeller rotates at high speed in the pump casing, and the water is thrown to the outer edge of the impeller along the blade flow channel under the action of centrifugal force, thereby obtaining energy. Centrifugal pumps are widely used in small and medium-sized industrial boiler systems due to their easy operation, low maintenance cost and high cost performance, especially for scenarios with relatively low flow and head requirements.
Multistage centrifugal pumps are based on single-stage centrifugal pumps. By connecting multiple impellers in series on the same pump shaft, the liquid flows through each impeller in turn to gradually obtain higher pressure. Each stage of the impeller pressurizes the liquid once, and the overall outlet pressure is determined by the number of stages and the design pressure head of each stage. Generally speaking, an increase in the number of stages can achieve a higher total pressure. This type of pump is particularly suitable for large power plants and high-parameter industrial boiler systems, and can meet the water supply needs of high head and large flow. Due to its efficient energy conversion mechanism, multistage centrifugal pumps excel in improving energy utilization efficiency and have become the preferred equipment for large steam production systems.
The working principle of positive displacement pumps is to transport liquid by changing the volume of the working chamber. Common types include reciprocating and rotary pumps. Reciprocating pumps use the reciprocating motion of the piston to periodically change the volume of the pump chamber to achieve the suction and discharge of liquid; rotary pumps force the liquid from the suction end to the discharge end through the mutual engagement of rotating parts such as gears and screws. The characteristics of positive displacement pumps are stable flow and unaffected by pressure changes. They are suitable for special process requirements with small flow and high pressure control accuracy, such as steam supply systems in precision chemicals, pharmaceuticals and other industries.
Turbine pumps use the thermal energy of steam to drive the turbine rotor, which in turn drives the feed pump impeller to rotate. This type of pump is commonly found in thermal power plants. Its biggest advantage is that it can make full use of the waste heat of steam generated by the boiler to achieve secondary utilization of energy and significantly improve the overall efficiency of the system. In addition, turbine pumps have high reliability and stability, and play an irreplaceable role in scenarios with extremely high requirements for continuous steam supply.
By Drive Mode
Electric drive: Electric pumps are the most common form of drive. The motor drives the pump shaft to rotate. It has the advantages of high control accuracy, rapid start-up, and convenient adjustment. It is suitable for most industrial occasions.
Steam drive: The steam generated by the boiler is used to directly drive the pump body. It is suitable for power plants and industrial enterprises with abundant steam resources, and can achieve cascade utilization of energy.
Diesel engine drive: As an emergency backup equipment, the diesel engine-driven feed pump starts when the power is off or the main drive system fails to ensure the continuous operation of the boiler system.
By Installation Layout
Horizontal pump: The horizontally installed feed pump has the characteristics of simple structure and convenient maintenance, but it occupies a large area and is suitable for industrial plants with ample space.
Vertical pump: The vertical pump adopts a vertical installation method, which has the advantages of saving space and easy integration. It is particularly suitable for occasions with limited space, such as boiler rooms in high-rise buildings.
By Functionality
Main feed pump: undertakes the main water supply task for daily operation of the boiler and needs to have high reliability and continuous operation capability.
Start/standby pump: put into use during the cold start phase of the boiler or when the main pump fails to ensure uninterrupted operation of the system.
Make-up pump: mainly used to supplement steam condensate, maintain the system water level stability, and improve the efficiency of water resource utilization.
By Pressure Rating
Based on different working pressures, boiler feed pumps can be divided into low-pressure pumps (<1.6MPa), medium-pressure pumps (1.6–3.8MPa) and high-pressure pumps (>3.8MPa). Pumps of different pressure ratings are suitable for boiler systems with different parameters. Users need to choose the appropriate pressure rating according to actual needs.
In industrial applications, the material selection of boiler feed pumps directly affects their service life and performance. Common materials for pump bodies include cast iron, carbon steel, and chrome steel. Cast iron has the characteristics of low cost and good casting performance, and is suitable for low-pressure and normal temperature conditions; carbon steel has high strength and toughness, and is suitable for medium and high pressure systems; chromium steel is often used in situations where high temperature, high pressure and corrosive media are handled due to its excellent corrosion resistance and heat resistance. In addition, the shell wall thickness needs to be designed according to the working pressure to ensure structural strength; the heat resistance of the material also needs to match the operating temperature of the boiler to avoid material performance degradation due to high temperature.
Choosing a suitable boiler feed pump requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors:
Flow and head: The flow of the boiler feed pump needs to be accurately matched with the rated evaporation capacity of the boiler, and a safety margin of 10%-15% is usually required to cope with load fluctuations. When calculating the head, in addition to considering the static head of the system, the pipeline resistance along the way, local resistance (such as valves, elbows) and the working pressure of the boiler drum must also be taken into account. By drawing the system resistance curve and comparing it with the pump performance curve, ensure that the pump operates in the high-efficiency area to avoid inefficient idling or overload operation.
Spatial layout: Horizontal feed pumps have the characteristics of simple structure and convenient maintenance, and are suitable for boiler rooms with ample ground space; vertical feed pumps are often used in compact industrial plants or multi-story buildings due to their small footprint and vertical installation to save space. When selecting, it is necessary to optimize the overall layout by combining factors such as the load-bearing capacity of the equipment foundation, the direction of the pipeline, and the later maintenance channel.
Water quality conditions: When the water quality is acidic or alkaline, the pump body material should be stainless steel or duplex steel to avoid chemical corrosion; for high-hardness water, silicon carbide mechanical seals and wear-resistant ceramic bearings are required to reduce the risk of wear. The calculation of net positive suction head (NPSH) needs to take into account water temperature, altitude and pipeline suction head. In order to prevent cavitation, it should be ensured that the net positive suction head (NPSHa) provided by the system is greater than the net positive suction head (NPSHr) required by the pump. It is usually recommended to retain a NPSH margin of 0.5-1.5 meters. The specific value depends on the working conditions and pump type.
Intelligent control: The intelligent feedwater pump system integrates variable frequency speed regulation (VFD), pressure sensor and PLC control system, which can adjust the flow rate in real time according to the boiler steam demand, and the energy saving efficiency reaches 20%-30%. The dry burning protection function monitors the water level of the water tank through the liquid level sensor, and automatically shuts down when it is below the threshold; the fault diagnosis module can record vibration and temperature abnormal data, upload them to the monitoring platform through the Internet of Things, realize preventive maintenance, and improve the overall safety and operation and maintenance efficiency of the system.
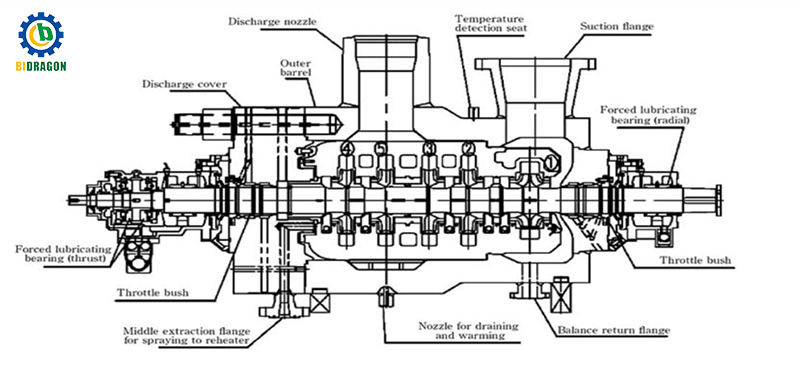
Correct installation is the basis for ensuring the efficient operation of the feedwater pump: a complete installation process can not only improve the performance of the equipment, but also reduce the subsequent maintenance costs, laying a solid foundation for the stable operation of the entire thermal system.
Base grouting and centering debugging: When installing the pump body, high-strength non-shrinkage grouting material is required to perform secondary grouting on the base to ensure that the base is fully fitted with the equipment base to form a stable support structure. Through the laser centering instrument, precise horizontal and centering debugging is carried out to control the concentricity error within 0.05mm, effectively reducing the vibration and noise caused by eccentric operation, and significantly extending the service life of key components such as bearings and seals.
Minimum flow protection valve setting: In order to prevent the impeller from idling and overheating or cavitation when the pump is running under low flow conditions, a pneumatic or electric minimum flow protection valve needs to be installed on the pump outlet pipeline. The valve needs to be accurately debugged according to the performance curve of the pump. When the flow rate is lower than 30% of the rated value, it will automatically open and return part of the medium to the deaerator or water tank to form a circulating cooling loop to ensure that the pump is always in a safe operating range.
Pipeline design: Reasonably design the suction and discharge pipelines, use large curvature radius elbows to reduce local resistance, and ensure that the vertical height of the suction pipeline meets the NPSH requirements of the pump. At the same time, a slow-closing check valve is installed near the pump outlet of the discharge pipeline to prevent the medium from flowing back to the suction port during shutdown and causing thermal shock; by optimizing the pipe diameter and layout, the resistance loss along the pipeline is reduced. It is usually recommended that the total resistance loss of the system be controlled within 0.1-0.3 MPa to improve the overall operating efficiency.
Regular maintenance is the key to extending the service life of the water feed pump:
Daily maintenance: Establish a daily inspection mechanism for the system, and record the changes in lubrication system pressure, oil temperature and oil quality in detail for each inspection. The lubricating oil should be replaced according to the cycle specified in the equipment manual. If the oil is emulsified, the impurities exceed the standard or the viscosity is abnormal, it needs to be replaced immediately. When inspecting the seals, focus on the wear of the dynamic and static rings of the mechanical seal. Once the leakage is found to exceed the standard value (usually ≤5 drops/minute), it should be replaced in time. The float level controller needs to be tested for sensitivity to simulate the changes in high and low water levels to ensure that the water level control accuracy is within the range of ±2cm.
Troubleshooting: For abnormal vibration, the vibration frequency and amplitude of each part of the equipment can be measured with the help of a vibration analyzer to distinguish whether it is caused by rotor imbalance (vibration frequency is the same as speed), bearing failure (characteristic frequency corresponds to bearing component defects) or foundation looseness (mainly low-frequency vibration). When the temperature rises, the motor winding temperature, bearing temperature and medium temperature need to be monitored synchronously. When it exceeds the rated value by 10%, the cooling system should be checked immediately after the machine is shut down. Flow fluctuation troubleshooting needs to be combined with pressure gauge and flow meter data to determine whether it is caused by pipeline blockage, impeller cavitation or insufficient pump cavitation margin, and take corresponding measures such as cleaning, air replenishment or adjusting the installation height.
Regular maintenance: The pump body needs to be disassembled for in-depth maintenance every six months, and the impeller mouth ring clearance needs to be measured with a micrometer. If the wear exceeds 0.3mm, it needs to be repaired or replaced by surfacing welding. In addition to checking the ball wear, the bearing also needs to detect the integrity and clearance value of the cage. The motor insulation performance test should select the appropriate megohmmeter test voltage according to the rated voltage of the motor. Usually, low-voltage motors use 500V~1000V, and high-voltage motors use 2.5kV~5kV. If the insulation resistance is lower than the specified value, it should be dried or rewound. After the overhaul, no-load and load test runs are required, and parameters such as vibration values, current, and flow are recorded to ensure that the equipment performance is restored to the factory standard.
The selection, installation and maintenance of boiler feed pumps is a systematic project. Different types of feed pumps have their own applicable scenarios: centrifugal pumps are suitable for small and medium-sized systems, multi-stage centrifugal pumps meet large-scale industrial needs, volumetric pumps solve special process problems, and steam turbine pumps achieve efficient energy utilization. In addition, the selection of drive mode, installation layout, functional classification and pressure level must be closely combined with actual working conditions. Through scientific and reasonable selection and standardized installation and maintenance, not only can the operating efficiency of the boiler system be improved, but also the safety and intelligence level of industrial production can be significantly improved. Therefore, it is recommended that users fully consider the system characteristics when selecting a boiler feed pump and consult professional engineers when necessary to achieve safe and efficient operation of the boiler system.