In the industrial field, boiler mountings are a series of key devices directly installed on the boiler shell. They are like the "safety guards" of the boiler and play a decisive role in the safe and stable operation of the boiler. These devices use precise control and protection mechanisms to ensure that the boiler avoids accidents under complex working conditions and ensures efficient energy conversion. With the continuous improvement of industrial production's requirements for energy supply stability and safety, understanding and correctly using boiler mountings has become a compulsory course for every industrial practitioner. So, among the many boiler devices, which are the truly "essential" boiler mountings? This is the core issue that this article will explore in depth.
Although boiler mountings and boiler accessories belong to the same boiler system, there are significant differences in many dimensions. From the installation position, boiler mountings are directly fixed on the boiler shell and are closely connected to the internal system of the boiler; while boiler accessories are mostly installed on pipes and auxiliary facilities connected to the boiler system to assist the operation of the boiler. In terms of core functions, boiler mounting parts focus on ensuring the safety and precise control of boiler operation, such as preventing overpressure and monitoring water level; boiler ancillary equipment focuses on improving the overall performance and operating efficiency of the boiler system, such as economizers to improve thermal efficiency and air preheaters to preheat combustion air.
Since boiler mounting parts are directly related to the safety of boiler operation, correctly identifying and installing these devices in a standardized manner is a basic requirement for industrial compliance. Violation of relevant installation standards and specifications may not only lead to serious safety accidents in the boiler, but also face severe penalties from regulatory authorities, causing huge economic and reputational losses to the company.
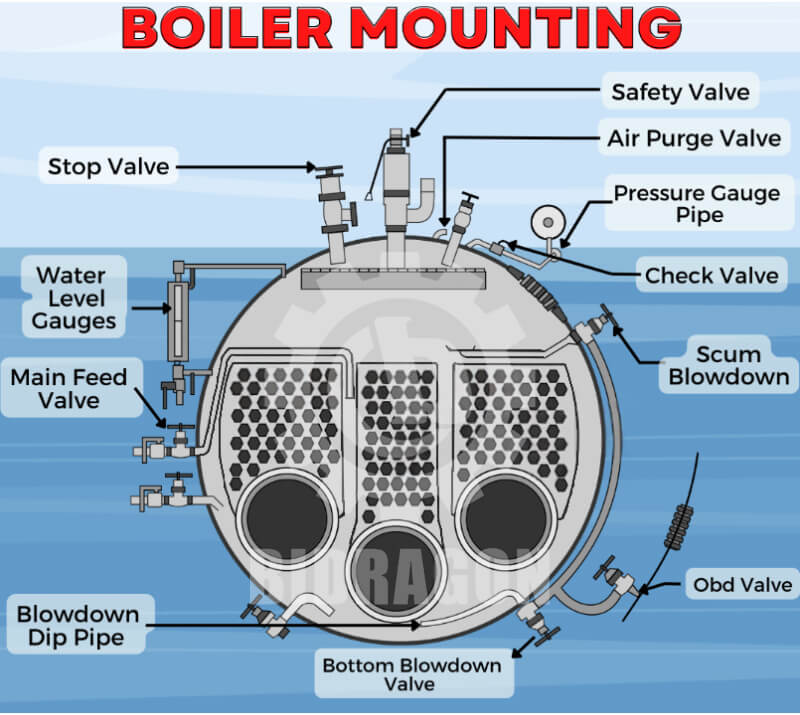
Boiler mounting parts have five key functions in industrial applications. First, the explosion-proof safety mechanism is its primary responsibility. Through safety valves, fusible plugs and other devices, energy is released in time when pressure or temperature is abnormal to prevent catastrophic accidents such as boiler explosions. Secondly, the water level and pressure control function ensures that the water level and pressure inside the boiler are always within a safe and reasonable range to ensure stable operation of the boiler. Furthermore, through precise control and adjustment, boiler mountings can effectively improve the operating efficiency of the boiler and reduce energy waste. In addition, these devices can also provide protection for the equipment, such as the drain valve discharges impurities to prevent equipment corrosion and damage, and facilitate daily maintenance and repair. Finally, the correct setting and operation of boiler mountings are necessary conditions to meet relevant international and domestic regulations and standards, such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standards and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards, to ensure that the company's production activities are legal and compliant.
The safety valve can be called the "first line of defense" for the safe operation of the boiler. Its core working principle is to automatically open and release overpressure steam when the steam pressure inside the boiler exceeds the preset value, thereby preventing the boiler from exploding due to excessive pressure. Common types of safety valves include spring type and lever type. The spring type safety valve controls the opening and closing of the valve through the elastic force of the spring, and has the characteristics of compact structure and easy adjustment; the lever type safety valve uses the principle of lever to balance the steam pressure through the weight of the heavy hammer, and has the advantages of sensitive action and high reliability.
Regardless of the type of safety valve, regular calibration is the key to ensure its normal operation. The calibration content includes checking whether the opening pressure and closing pressure of the valve meet the standards, and whether the sealing performance of the valve is good. Generally speaking, the safety valve should be calibrated at least once a year. Under special working conditions, the calibration cycle may need to be shortened to ensure that it can accurately operate at critical moments and play a protective role.
The water level is an important parameter affecting the safe operation of the boiler. Too low a water level may cause the boiler to dry burn and cause serious accidents; too high a water level will affect the steam quality. The function of the water level indicator is to display the boiler water level in real time and provide operators with intuitive and accurate water level information, thereby preventing dangerous situations such as low water level dry burning.
Common types of water level indicators include glass tube type and magnetic flap type. The glass tube water level gauge has a simple structure and directly observes the water level through a transparent glass tube, but it has the disadvantages of being fragile and relatively low in safety; the magnetic flap water level gauge uses the magnetic principle to convert water level changes into flap color changes, which has the advantages of clear display, safety and reliability, and easy long-distance observation. In order to further improve the accuracy and automation of water level control, the water level indicator usually needs to be linked with the water level automatic control system. When the water level exceeds the set range, the automatic control system can take timely measures, such as starting water replenishment or drainage operations, to ensure that the water level is stable in a safe range.
The pressure gauge is like a "heartbeat meter" that monitors the operation of the boiler. It can provide real-time feedback on the internal pressure of the boiler, help operators understand the operating status of the boiler, and promptly detect pressure abnormalities and take corresponding measures. The Bourdon tube pressure gauge is a commonly used type of pressure gauge in industrial boilers. Its working principle is to use the Bourdon tube to deform under pressure, and convert the deformation into the deflection angle of the pointer through the transmission mechanism to display the pressure value.
In actual operation, there is a close pressure coordination mechanism between the pressure gauge and the safety valve. The pressure gauge provides a pressure reference for the action of the safety valve. The operator reasonably sets the opening pressure of the safety valve according to the pressure value displayed on the pressure gauge; when the boiler pressure rises to the opening pressure of the safety valve, the safety valve automatically opens to release the pressure. At the same time, the pressure gauge monitors the pressure change in real time to ensure that the pressure drops to a safe range. The two cooperate with each other to jointly ensure the stability of the boiler pressure.
The steam stop valve is mainly used to control the flow of steam from the boiler to the main steam pipeline, and is a key control component for the boiler steam output. When the boiler is shut down for maintenance or the system needs to be isolated, closing the steam stop valve can effectively cut off the steam path, prevent steam leakage, and provide a safe working environment for maintenance personnel; during normal operation, by adjusting the opening of the steam stop valve, the steam flow can be controlled to meet the steam requirements of different production processes.
The installation position of the steam stop valve is very critical, and it should generally be installed near the boiler outlet and in a place that is easy to operate. In terms of maintenance, it is necessary to regularly check the sealing performance of the valve, the flexibility of the valve stem, etc., to prevent the valve from leaking, sticking, etc., and ensure that it can be opened and closed normally when needed.
The fusible plug is a special device for emergency thermal protection, usually installed in the area directly contacted by the flame in the boiler. When the boiler water level is too low and the flame directly heats the shell, causing the local temperature to be too high, the low melting point alloy in the fusible plug will melt, thereby releasing steam, reducing the shell temperature, and preventing the shell from being damaged due to overheating. It can also play a role in extinguishing fire.
In practical applications, fusible plugs are usually used in conjunction with water level alarms. When the water level drops to a dangerous position, the water level alarm first sounds an alarm to remind the operator to take measures; if the operator fails to handle it in time, the water level continues to drop, causing the fusible plug temperature to rise to the melting point, and the fusible plug automatically operates to release steam, providing the last protective barrier for the boiler.
The main function of the blowdown valve is to discharge the sediment, impurities and high concentration of salt accumulated in the boiler water to prevent these substances from scaling and corroding the equipment in the boiler, thereby extending the service life of the boiler and ensuring the thermal efficiency of the boiler.
Regular blowdown is an important part of boiler operation and maintenance. Its operation process includes selecting the appropriate blowdown time, controlling the blowdown volume and blowdown time, etc. During the sewage discharge process, it is necessary to pay attention to the temperature changes of the sewage pipe to avoid water hammer caused by too fast sewage discharge. Common sewage valves are fast-opening and slow-opening. The fast-opening sewage valve has a fast sewage discharge speed and is suitable for quickly removing a large amount of impurities; the slow-opening sewage valve has a relatively slow sewage discharge speed and is suitable for fine sewage discharge and adjustment of sewage discharge volume. The appropriate sewage valve type should be selected according to the actual working conditions.
The function of the feed water check valve is to prevent the water in the boiler from flowing back to the feed water system and protect the water pump and other equipment in the feed water system. If there is no feed water check valve, when the boiler pressure is higher than the feed water system pressure, the water in the boiler will flow back, which may cause the water pump to reverse and be damaged, and it will also cause system pollution, affecting the water quality and the normal operation of the boiler.
Feed water check valves can be divided into two types: automatic control and manual control. The automatically controlled water supply check valve can automatically open and close according to the direction of water flow without manual intervention, and is easy to operate and responds quickly; the manually controlled water supply check valve requires the operator to manually operate the valve switch. Although the flexibility is relatively low, it has certain advantages in some special cases, such as equipment maintenance or commissioning.
Each boiler mounting plays a unique and indispensable role in safety control. In terms of pressure control, the safety valve automatically releases pressure when the pressure exceeds the limit, and the pressure gauge monitors the pressure in real time. The two cooperate with each other to ensure that the boiler pressure is stable within a safe range; in terms of water level maintenance, the water level indicator displays the water level in real time, and the fusible plug starts protection when the water level is too low and the temperature is too high to ensure the normal boiler water level; in terms of steam control, the steam stop valve accurately controls the steam flow and passage; in terms of impurity management, the drain valve discharges impurities in time to prevent scaling and corrosion; in terms of fluid direction control, the water supply check valve ensures one-way flow of water supply and protects the water supply system. These mountings work together to build a complete safety control system to ensure safe and stable operation of the boiler.
To ensure that boiler mountings are always in good working condition, regular inspection and maintenance are essential. Generally speaking, key mountings such as safety valves and pressure gauges should be visually inspected once a month to check for leaks, damage, etc.; functional tests should be conducted every six months to ensure that their operation is accurate and reliable. The water level indicator should be flushed once a week to prevent dirt from clogging and affecting the display effect; a comprehensive inspection should be conducted once a year, including display clarity, linkage performance with the automatic control system, etc.
In terms of maintenance and verification procedures, they should be strictly carried out in accordance with relevant standards and specifications. For example, the verification of the safety valve should be entrusted to a qualified professional organization, and a verification report should be issued after the verification, and the safety valve should be sealed with lead; the verification of the pressure gauge also requires the use of a standard pressure source and precision measuring instruments to ensure accurate measurement.
In daily operation, operators should also pay close attention to common fault warning signals of boiler mountings. For example, safety valve leakage, abnormal jitter of the pressure gauge pointer, blurred display of the water level indicator, etc., once an abnormality is found, the machine should be stopped for inspection immediately, and the fault should be handled in time to avoid the expansion of the fault and cause a safety accident.
As the core guarantee for the safe and efficient operation of industrial boilers, the importance of boiler installation parts is self-evident. From the explosion-proof protection of safety valves to the balance maintenance of water level indicators, from the pressure monitoring of pressure gauges to the impurity management of drain valves, each installation part plays a key role in its respective position. Correct selection, standardized installation and regular maintenance of boiler installation parts are not only necessary measures to ensure the safe and stable operation of boiler equipment, but also an important responsibility for enterprises to follow industry standards, ensure the safety of personnel and reduce economic losses.
Industrial enterprises should attach great importance to the management of boiler installation parts, operate in strict accordance with relevant standards and specifications, establish and improve the maintenance system of installation parts, strengthen the training and education of operators, and improve safety awareness and operating skills. Only in this way can the role of boiler installation parts be fully utilized, reliable energy guarantee can be provided for industrial production, and sustainable development of enterprises can be achieved.