In the huge system of industrial production, steam boilers play a vital role, as a key energy supply equipment, it is for all types of industrial operations to deliver a constant flow of energy. Due to different industries, different working conditions on the energy needs of different, steam boilers have developed a rich variety of types. This article will introduce the different types of steam boilers in detail to help readers gain a deeper understanding of their characteristics and application scenarios, so that they can make more appropriate decisions in the actual selection and use.
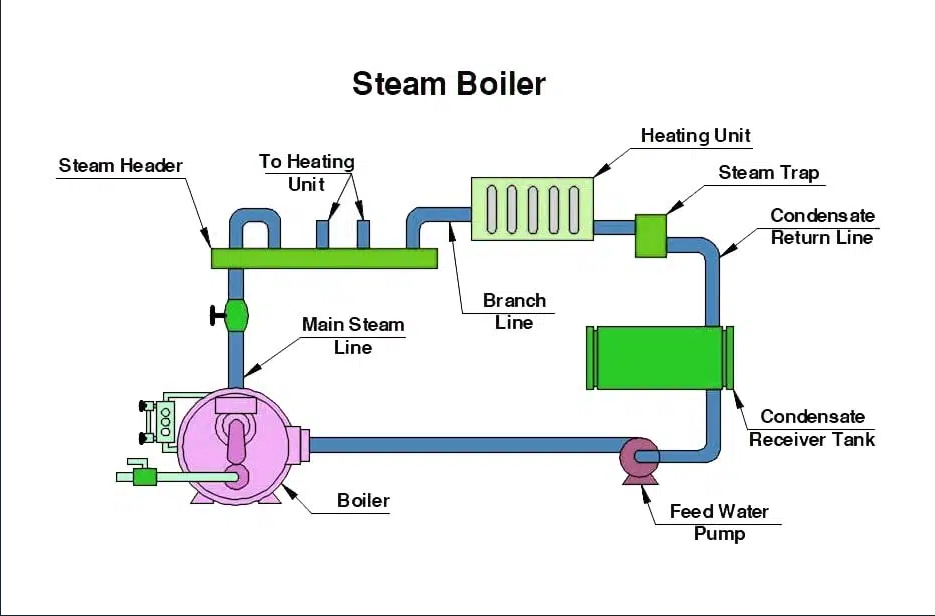
Steam boilers are large pressure vessels whose core mission is to provide energy for industrial operations. Energy is converted and supplied by heating water to boiling under subcritical pressure to produce steam through a complex and delicate fuel system.
Given the high pressure operation and high steam output of steam boilers, there are strict codes of practice for their operation in many areas. The operation of steam boilers must be carried out in the field by certified and licensed operators to ensure the safety and stability of the operation of the equipment.
From a design perspective, firetube and watertube are the two most common types of steam boilers. These two designs differ significantly in their construction and heat transfer methods, which also determines their suitability for different application scenarios.
Depending on the structure, steam boilers present a diverse range of types. Among them, the fire tube boiler is characterized by the flow of high temperature flue gas inside the fire tube, which transfers the heat to the water outside the tube, and has a more compact structure, is easy to operate, and is commonly used in small-scale industrial production and heating fields. Water tube boilers, on the contrary, the water flows inside the water tube to be heated, has the advantages of high thermal efficiency and large evaporation capacity, suitable for large industrial enterprises on the large amount of steam demand scenarios. Shell boiler as a common one, its pot shell housing vapor system, the furnace chamber as combustion space, the overall structure is simple, easy to install and maintain, in some of the higher space requirements of the place widely used. Each structure type shows different performance advantages by virtue of its unique construction characteristics to adapt to all kinds of production and life needs.
Different types of steam boilers have significant differences in adaptability. For example, small vertical steam boilers, compact size, start quickly, can quickly provide steam for laboratories, small laundries, etc., to meet the energy needs of such working conditions on the steam volume demand is small, but the response speed requirements of high energy needs. The large horizontal steam boiler, evaporation capacity and continuous stability, in the chemical industry, paper and other large-scale industrial production, can be a long time, large-scale supply of steam to ensure the stable operation of the production line. They play different roles in various industries based on their own characteristics, covering a wide range of applications, from meeting basic life services to supporting large-scale industrial operations.
Fire tube and water tube are the two main types of tubes used in steam boilers. In a fire tube boiler, high-temperature combustion products flow inside the fire tube, and the heat is transferred to the water outside the tube through the tube wall. This type of tube is relatively simple in structure and has low manufacturing and maintenance costs, but the heat transfer efficiency is relatively limited due to the limited travel of flue gases flowing inside the tube. The water tube boiler water flows in the water tube, high temperature flue gas flushing outside the water tube, water tube surface area is large, the heat exchange is sufficient, greatly improving the heat transfer efficiency. At the same time, the arrangement of the water tube in a variety of ways, can be optimized according to the needs of different heat load design, which significantly improves the overall performance of the boiler, so that it is more suitable for the higher requirements of steam production and thermal efficiency of industrial scenarios.
Steam boilers use a wide variety of fuel types, including natural gas, fossil fuels, coal, electricity, wood and so on. Natural gas as a fuel has the advantages of clean combustion, quick startup, high thermal efficiency, and less pollutants after combustion, which meets the current environmental protection requirements, and is widely used in centralized urban heating and industrial production with high environmental requirements. Fossil fuels such as heavy oil, high energy density, in some energy supply to fossil fuel-based and relatively low environmental requirements of the region, can provide continuous and stable energy for the steam boiler. The cost of coal is relatively low, rich resource reserves, but the combustion process will produce more pollutants, need to be equipped with complex environmental protection equipment. Electrically heated steam boilers, which are simple to operate and have no exhaust emissions, are suitable for places with sufficient power resources and extremely stringent environmental requirements, although their operating costs are usually higher. Wood, as a renewable fuel, has some applications in some forestry resource-rich areas, but the combustion efficiency is relatively low and the stability of wood supply is required. Each of these fuels has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, environmental friendliness and efficiency, so users can choose flexibly according to the actual situation.
According to the different pressure output, steam boilers can be divided into low-pressure boilers and high-pressure boilers. Low-pressure boilers are generally lower pressure range, usually for occasions that do not require high steam pressure, such as small food processing enterprises for steaming, sterilization, its principle of operation is relatively simple, equipment costs and operation and maintenance costs are low. High-pressure boilers can produce higher pressure steam, the pressure range is much higher than the low-pressure boilers, commonly used in large-scale chemical industry, power generation and other industries, in these industries, high-pressure steam to drive the turbine and other large-scale equipment operation, to achieve efficient conversion and utilization of energy. The working principle of high-pressure boilers is even more complex, and there are extremely high requirements for equipment materials, manufacturing processes, and safety measures to ensure stable and safe operation under high-pressure environments.
Electric boilers generate heat with the help of electric elements, which is a highly efficient and fast heating method. Since there is no fuel to burn, it is a cleaner and more environmentally friendly option. In addition, electric boilers are durable, easy to clean, and require low maintenance. However, electric boilers do have one concern, which is that they are prone to scale buildup in the storage tank, which needs to be dealt with on a regular basis. Because of their precise temperature and pressure control capabilities, electric boilers are commonly used in research facilities and laboratories with high steam requirements.

Gas boilers are fueled by natural gas or propane and are more efficient than regular boilers. The fuel is delivered to the unit through an external supply source directly connected to the boiler. The design of a gas boiler determines how the heat is distributed and it is suitable for industrial production as well as low pressure applications.
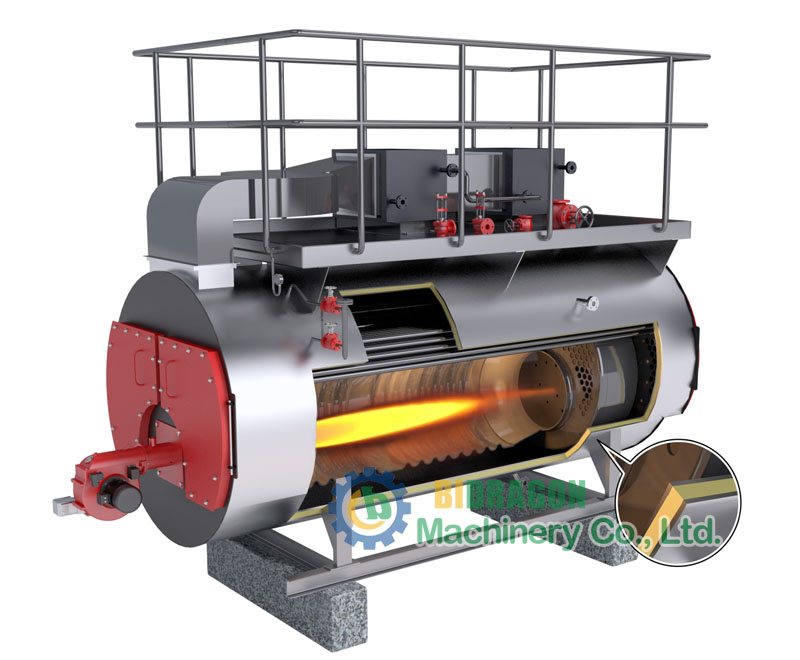

Oil-fired boilers work on a similar principle to gas-fired boilers, with the difference that oil-fired boilers burn oil in a combustion chamber to heat water. These boilers can have efficiencies in excess of 90%, and although they cost more than gas boilers, they typically last twice as long. However, oil-fired boilers have the obvious disadvantage of needing to be equipped with an oil tank and refueled frequently to ensure a steady supply.

Biomass boilers utilize organic materials such as wood chips and agricultural residues as fuel. The combustion of these biomass materials releases heat, which in turn is transferred to the water in the boiler, ultimately producing steam. Biomass boilers are a sustainable option because their combustion process produces low greenhouse gas emissions and are commonly used in some manufacturing, forestry, and industries that are actively transitioning to renewable energy.
Low pressure steam boilers operate at pressures between 10 - 15 psi and temperatures of 149°C (300°F). Low-pressure boilers are ideal when constant temperatures are more desirable than sudden temperature changes. In addition, low-pressure steam boilers are able to supply steam faster than high-pressure boilers, an advantage that makes them popular in many scenarios.
High-pressure steam boilers drive machinery and equipment by generating extremely high pressures. The power comes from the pumps that deliver the high pressure steam to the circulating system. Generally, boilers capable of generating 15 - 800 psi and temperatures above 250°F (121°C) can be characterized as high pressure steam boilers. To ensure safe and efficient operation, the pressure and temperature of a high-pressure steam boiler need to be rigorously checked on a regular basis. Their high-pressure loads can be categorized as batch loads for short-term needs and continuous loads for long-term needs.
Firetube Boilers
Firetube boilers consist of a large shell in which the hot gases produced by combustion are passed through one or more boiler tubes connected to the front and rear boiler plates. The most common type of firetube boiler is the Scottish marine firetube boiler, which utilizes one large furnace tube and many smaller boiler tubes. Hot gases from the combustion process pass through these tubes, transferring heat to the surrounding water, which heats up to the boiling point and in turn produces steam. In addition, the addition of a coal economizer to a fire tube boiler can effectively increase its efficiency and heat recovery. Because of their ability to produce steam quickly and cope with varying load demands, fire tube boilers are commonly used in small industrial facilities such as breweries.
Water tube boilers are designed to be the opposite of fire tube boilers in that water flows inside the smaller diameter boiler tubes while combustion gases surround the outside of the tubes, transferring heat to the water inside. In the water tube boiler design, the boiler tubes transfer the heated water between the lower steam ladle (mud ladle) and the upper steam ladle (steam ladle), and the resulting steam accumulates in the upper steam ladle. Heat is generated in the hearth area and transferred to the water through two main areas, the hearth area and the convection area. Water tube boilers generate high pressure steam through tangential pressure (i.e., annular stress) in the tubes, which is similar to the pressure exerted on the hoop of a barrel when it is filled with water. Because of their high efficiency and ability to withstand high pressures, water tube boilers are commonly used in industries such as large-scale manufacturing where the demand for steam and power is constant and high.
Shell boilers have a shell, usually made of steel, around their heat transfer surface. The path that the heat takes before it is expelled depends on the combination of pipe layouts used. What is commonly known as a flue boiler is a shell boiler, which contains a long water tank and fire tubes which transfer heat from the furnace or combustion chamber to the water in the tank. The Cornish boiler, which is the oldest example of this type, is a long cylinder with a larger internal flue or pipe for containing the heat or flame, and was later superseded by the Lancashire steam boiler with two fire flues. Shell steam boilers, also known as shell and tube boilers, are a simple type of boiler capable of producing steam efficiently and economically.
A condensing boiler is designed to extract additional heat from the flue gas, thereby dramatically improving energy efficiency. It does this by cooling the flue gas to the point where water vapor condenses, causing the water vapor to release latent heat. Due to its ability to improve thermal efficiency and low environmental impact, condensing boilers are commonly used in industries such as food processing.
The main function of a waste heat boiler is to recover heat that would otherwise be wasted in industrial processes. It captures waste heat from industrial processes such as exhaust gases, heat from chemical reactions and high temperature flue gases. Waste heat boilers play an important role in industries that strive to maximize energy use and minimize waste, such as steel production, chemical processing, and cement manufacturing.
The Assembled Boiler is a factory-assembled unit designed for quick installation and easy operation. It is available in a variety of configurations, including fire tube and water tube types. For businesses, hospitals, schools, hotels, and small industrial locations with limited space or resources, an assembled boiler is a good choice because it produces steam reliably and efficiently.
The term “industrial boiler” covers a wide range of boiler designs, sizes, and capacities. These boilers meet the needs of heavy industries such as chemical manufacturing, petrochemical processing, and paper production. Industrial boilers are available in both fire tube and water tube types and are often equipped with emission reduction technology, advanced control systems and heat recovery components. Because of their ability to handle complex industrial processes and withstand high steam pressures, industrial boilers are designed for industrial applications.
Different types of steam boilers use different heat sources. Boilers fueled by natural gas, oil, or coal produce a flame or hot gas by burning the fuel, while electric boilers rely on electrical components to generate heat.
In a fire-tube boiler, heat is transferred directly to the surrounding water; in a water-tube boiler, heat is transferred to the water inside the tubes by means of combustion gases on the outside of the tubes; and in an electric boiler, the water is heated by the direct contact of an electric element with the water.
When water is heated to the boiling point, it undergoes a phase change and is converted to steam.
The generated steam is piped to various application points to meet different industrial and commercial needs.
Burner
The burner is where the fuel is mixed with air and ignited, and through this process heat is generated to provide a source of energy for the generation of steam.
The combustion chamber is the area where the fuel is burned and where it is fully combusted, releasing a large amount of heat.
Heat Exchanger
The function of the heat exchanger is to transfer the heat from the combustion gases to the water in the boiler without mixing the water and the combustion gases, realizing an efficient conversion of energy.
As water heats up, its volume expands, and the expansion tank exists to cope with this pressure change and to guarantee stable operation of the system.
The steam control system is responsible for regulating the temperature and pressure of steam to ensure that the steam produced meets the requirements for use.
In the manufacturing industry, steam boilers are widely used in heating, sterilization and other processes to provide the necessary conditions and safeguards for the production of products.
Steam is often used to drive turbines to produce electricity, and is an important energy carrier in the power generation process.
In food processing, steam is used to cook food, clean equipment, and sterilize equipment to ensure food quality and safety.
Many buildings utilize steam heating systems to provide warmth and comfort indoors during cold weather.
There are a wide variety of steam boiler types, each with its own unique characteristics and application scenarios. From fuel type to pressure output, from structural design to special functions, different types of steam boilers play an indispensable role in various fields of industrial production and social life. Understanding the differences between these steam boiler types helps the relevant industries to choose the most suitable steam boiler according to their own needs in practical applications, thus realizing efficient, safe and economical production operations. With the continuous development of technology, steam boilers are also continuing to innovate and improve, the future will bring more possibilities and value for various industries.