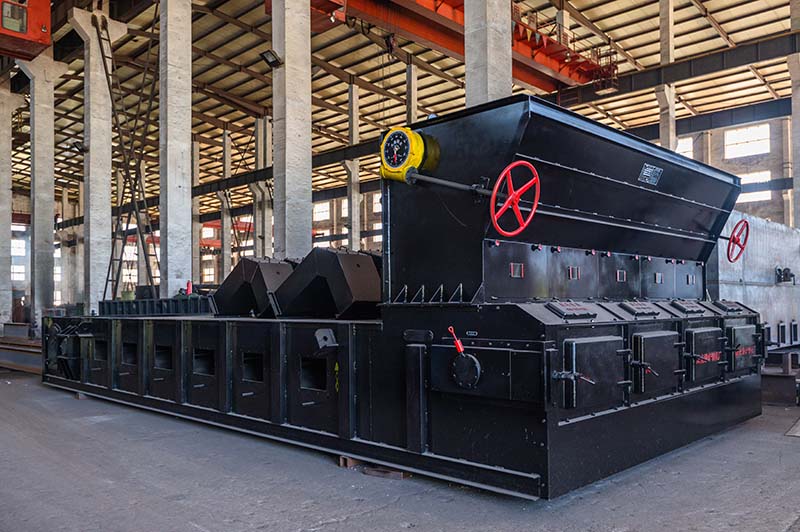

The chain grate boiler is a layer-burning furnace with a high degree of mechanization. Its structure is relatively simple, the manufacturing and installation process requirements are not high, and the grate does not leak coal. It is named because its grate is similar to a chain track. It is a furnace type that is widely used in industrial boilers. The operation process of the chain is from the starting end to the heat collection and absorption area. The heat released by the fuel in the middle section is basically not helpful to the efficiency. Therefore, the coal distribution, coal seam thickness and chain speed are all very critical. Here are some common faults and troubleshooting methods of the chain grate boiler body or auxiliary equipment.
The structure and working principle of the chain grate boiler are as follows:
The fuel supply system includes equipment such as excavators, storage hoppers, charging barrels, conveyors, and screw feeders. These components can flexibly, quantitatively and automatically supply fuel to the boiler. In addition, the fuel supply system may also be equipped with a weight scale to measure the amount of fuel consumed by the boiler.
The fuel supply hopper is located outside the combustion chamber area. Under the action of gravity, the fuel is evenly spread on the grate surface and then enters the combustion chamber of the boiler with the chain grate. During the movement of the grate, different stages of fuel combustion are carried out in sequence and occupy a specific area in the length direction of the grate. The ash produced after the combustion process is pushed into the ash collecting hopper by the ash removal device.
The combustion process of fuel is a chemical reaction between the chemical elements in the fuel and oxygen, thereby generating light and heat (combustion is an oxidation process). The main oxidant is oxygen obtained from the air, which is fed into the chain grate combustion chamber through the wind box. The combustible elements in the fuel (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, etc.) undergo oxidation reactions during the combustion process, and the products produced are called flue gas.
The heat released during the combustion process is transferred to the steam generation tubes arranged around the combustion chamber. The water in the steam generation system tubes is heated to boiling point to generate steam. The resulting steam-water mixture flows upward and collects in the steam drum. The steam drum is used to separate the steam from the steam-water mixture. The unevaporated water in the drum is returned to the steam generating tubes through a downcomer system located outside the water wall (to avoid heat absorption). The water flowing in the downcomer is not heated and has a greater density than the steam-water mixture in the steam generating tubes, forming a water column weight difference, which promotes the natural circulation of the fluid in a closed loop.
However, when the working pressure of the boiler reaches the critical or supercritical state, a circulating pump must be used to assist the water flow in the steam generating tubes. The steam discharged from the drum is saturated steam. If high-quality steam is required, the saturated steam can be heated to high-temperature superheated steam through a superheater.
The flue gas generated by fuel combustion still contains a lot of heat energy after passing through the convection tube bundle of the boiler. Therefore, in the boiler system, a water heating device (economizer) and an air heater (air preheater) are set up to utilize this part of the heat source to avoid energy waste and ensure the highest boiler efficiency.
The water from the water supply tank is deaerated (removing dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide in the water) and then pumped into the economizer. Here, water is heated to the appropriate temperature before entering the boiler drum. However, the economizer should not be too large to prevent the accidental vaporization of water in the economizer, which would create a large resistance in the boiler's water supply pipe.
Outside air is fed into the air preheater by a fan to maximize the use of the heat in the exhaust flue gas. The flue gas temperature after the air preheater is about 110-140°C. The flue gas temperature should not be too low to prevent the sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides in the flue gas from oxidizing into acids, causing corrosion of the flue pipe due to condensation.
The dust removal system can use bag filters, electrostatic precipitators or wet scrubbers to treat the dust from the boiler. These dust removal equipment are designed to filter and separate dust particles in the flue gas to ensure that the exhaust gas meets all environmental standards when it is discharged through the flue.
Induced draft fan is a device that extracts flue gas from the boiler combustion chamber and pushes the flue gas into the flue and discharges it to the environment. The induced draft fan is also a device that maintains negative pressure in the combustion chamber to prevent positive pressure accidents, as positive pressure may be dangerous to operators and boiler systems.
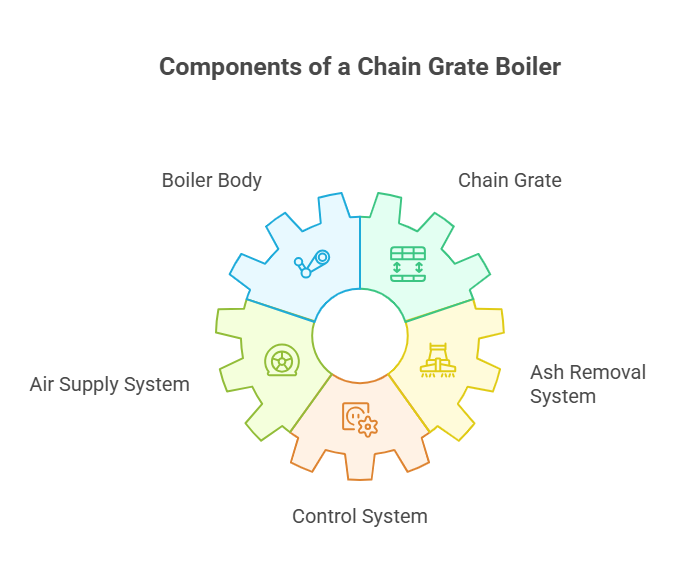
A typical chain grate boiler consists of the following main components:
Boiler body: includes steam drum, water wall and convection tube bundle.
Chain grate: a mobile grate mechanism that transports fuel through the combustion zone.
Air supply system: primary and secondary air fans provide oxygen for combustion.
Ash removal system: collects and removes ash produced by the boiler.
Control system: realizes automatic operation, temperature/pressure control and fault alarm.
Chain grate boilers excel at burning solid fuels such as coal, biomass pellets, and peat. They are best suited for burning fuels with uniform particle sizes. These boilers can use different types of coal and biomass fuels such as wood pellets and rice husks.
|
Fuel Type |
Characteristics |
Efficiency |
|
Coal (Anthracite, Lignite) |
High calorific value, low moisture |
High |
|
Biomass Pellets |
Uniform particle size, medium calorific value |
High |
|
Peat |
Variable moisture, medium calorific value |
Medium |
Biomass includes: rice husk, bagasse, sawdust, palm shell, etc.
Coal includes: bituminous coal, lignite, etc.
Waste includes: jute waste, fabric scraps, etc.
Its fuel use flexibility is suitable for different industries.
Chain grate boilers are widely used in the following fields:
Textile and garment industry: dyeing, printing, finishing.
Food processing plants: cooking, sterilization, drying.
Chemical industry: reaction heating, distillation.
Paper mills: pulping, drying, sizing.
Building materials industry: cement maintenance, brick manufacturing.
Their ability to use low-cost fuels makes them particularly attractive in emerging markets.
Advanced structure: The boiler is a single-drum fast-loading three-pass water-fire tube boiler with a large heating surface and high thermal efficiency.
Compact design: The boiler has a compact structure, a reasonable water circulation design, and a quick start.
Advanced grate: The advanced chain grate is reliable, with less coal leakage, energy saving, and reduced installation and maintenance workload; the long arch increases the effective area of the grate, has good adaptability to coal types, and fully burns the fuel.
High efficiency: The grate is equipped with a reasonable combustion air distributor to fully burn the fuel and improve equipment efficiency.
Pure steam: The steam dryness is more than 96%.
High degree of intelligent control: The boiler has multiple interlocking safety controls such as pressure, temperature, and water level; it has a high degree of mechanization and is easy to operate.
Easy installation: The chain grate boiler is shipped as a whole from the factory, and the installation period is extremely short.
|
Feature |
Traveling Grate Boiler |
Fixed Grate Boiler |
Fluidized Bed Boiler |
Gas/Oil Boiler |
|
Fuel Flexibility |
High |
Medium |
High |
Low |
|
Automation Level |
High |
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
Initial Investment |
Medium |
Low |
High |
Medium - High |
|
Fuel Cost |
Low |
Low |
Low |
High |
|
Efficiency |
High |
Low - Medium |
High |
High |
Chain grate boilers strike a balance between fuel economy, efficiency and automation, making them a popular choice in many industrial fields.
The grate of the chain grate boiler is a rotating combustion device. Due to the harsh working environment, it is very easy to get stuck and stop. In daily applications, the grate has many faults and requires a lot of maintenance, which affects the normal use of the boiler. The fault manifests itself as: the motor current suddenly increases, the grate safety spring bounces or the safety clutch operates, and an abnormal impact sound is emitted.
The manufacturing quality of boiler materials is an important cause of grate failure. Improper adjustment of the chain adjustment screws on both sides of the chain grate results in different chain lengths on the left and right sides. The flatness of the front and rear axes of the grate affects the running resistance and force uniformity of the grate, which can easily cause the grate to deviate and break. The grate is broken, and one end is exposed on the grate surface. When it reaches the slag plate, it is sometimes stuck by the tip of the slag plate, and sometimes the grate falls off completely. When it reaches the slag plate, the tip of the slag plate sinks and supports the grate, hindering the normal operation of the grate. In severe cases, the grate will be stuck or pulled off.
Common faults of the furnace wall include coking, cracks, tilting, loose bricks, partial detachment, the furnace pipe is stuck by hard objects at the wall, and the sealing asbestos rope is burned.
When the chain grate boiler is working normally, if outside air enters the furnace, the carbon dioxide content in the flue gas will decrease, the oxygen content will increase, the combustion chamber will become positive pressure, and the boiler bracket or the outer skin of the furnace wall will heat up or even burn red, which indicates that there are many cracks in the furnace wall and serious air leakage.
The lining bricks of the furnace wall are cracked or partially peeled off, which may damage the furnace wall and the hanging brick hanger of the combustion chamber. The reasons include: improper furnace drying after maintenance, incorrect methods of heating or stopping the furnace, poor quality of refractory materials, poor construction quality, unreasonable design (furnace wall hinders the normal expansion of heated parts), excessive thermal strength, insufficient cooling of the hanger, severe wear of the furnace wall (wear thickness exceeds 1/3 of the original thickness), frequent operation of the boiler under positive pressure, excessive furnace temperature, severe coking of the furnace wall, and spraying water on the furnace wall when coking, etc.
When the chain grate boiler is running, the grate surface may burn unevenly, which is specifically manifested as: large pieces of coal are blocked at the coal gate; the speed of the coal feeder and the grate are adjusted too frequently; the opening height ratio of the coal gate is the same; the air volume on both sides is uneven, one side is large and the other side is small; the coal seam is unevenly distributed; the coal feeder is improperly adjusted; the coal seam control is unreasonable; the air supply regulation performance of the wind chamber is poor; the temperature of the main combustion area is not high; the air volume on both sides is large, and the middle is red; the coal seam on the grate is sloped; there is fire on one side of the grate fire bed and no fire on the other side, forming a triangle; the coal particles on both sides are large and the air volume is also large, and the ignition is early; the slag on both sides of the furnace wall hinders the normal movement of coal; the flame length is uneven; coal is piled in front of the arch; coal coking under the arch, etc.
Soot blowers are equipment that blows away the ash on the heating surface of the boiler to keep the heating surface clean, so as to improve the heat transfer effect, ensure the thermal efficiency of the boiler, and prevent the heating surface from coking. It plays a very important role in preventing secondary combustion in the tail flue and air preheater, and helps to improve the safe and economical operation level of the boiler unit.
Common faults include: boiler extinguishing, coking, sootblower pipe burning and smashing or jamming the slag crusher, air preheater blocking or jamming. When the boiler is started, shut down and running at low load, the furnace flame burns unstably. If the air volume and pressure are not adjusted in time, the boiler may extinguish. After the sootblower pipe is burned due to a fault and cannot be withdrawn, it will directly fall into the slag crusher at the bottom of the cold ash hopper, causing the slag crusher to jam or damage, resulting in the boiler being unable to discharge slag normally.