Industrial boilers play an extremely important role in the modern industrial system, providing indispensable power to the manufacturing operations of many industries. Have you ever wondered how a single industrial boiler can power an entire manufacturing plant? Let's take a closer look at the world of industrial boilers.
.jpg)
An industrial boiler, also known as an industrial steam generator, is capable of producing steam at much higher pressures than the pressure cookers we use every day. In order to withstand extreme pressures ranging from a few bar to hundreds of bar, an industrial boiler is usually constructed from rows of thick steel plates welded together and must be extremely robust in its design. Because of the enormous pressures they carry, extreme care must be taken in designing and operating them, as any slight error can have serious consequences.
Industrial boilers are widely used in the food and beverage, paper, chemical, textile and animal feed industries. In the energy sector, the high pressure steam produced by boilers is combined with turbines to generate electricity to power people's lives.
In a fire tube boiler system, hot combustion gases pass through tubes surrounded by water. Heat is transferred from the gas to the water to produce steam. Due to their design limitations, fire tube boilers are usually suitable for low to medium pressure application scenarios. These boilers are often used in textile and food processing industries as well as some small power plants.
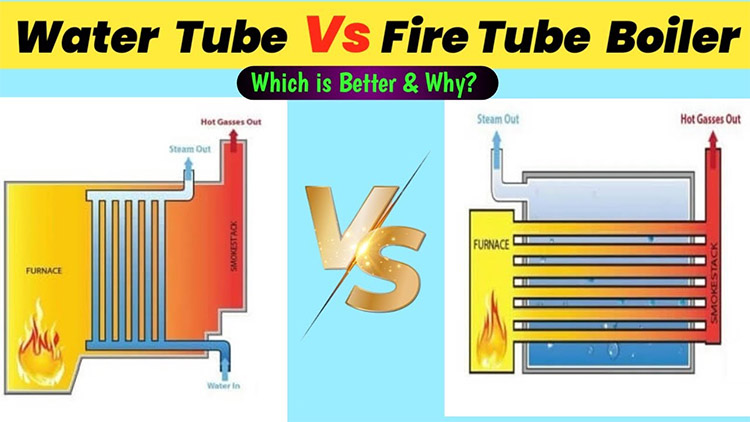
In contrast to fire tube boilers, in water tube boilers, water circulates in tubes heated by external combustion gases. This configuration allows them to withstand higher pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications such as chemical processing, oil refining, and power generation.
Modular boilers consist of a number of smaller, independently operated units that work together to meet different steam requirements. These boilers are typically extremely efficient, producing steam quickly and flexibly adapting to fluctuations in load. The reliability of modular boilers is also significantly enhanced because operators can perform maintenance or repairs on individual units without shutting down the entire system.
Waste heat recovery steam generators recover waste heat from gas turbines, thermal oxidizers or other processes to produce steam. Commonly used in combined cycle power plants, ethanol production facilities, and combined heat and power (CHP) applications at colleges and universities. Waste heat recovery steam generators are also popular in desalination plants and other energy intensive industries.
The working principle of an industrial boiler system is based on some basic scientific concepts and is relatively simple in construction. The components of the boiler system are installed in various locations, for example, the heat source is housed in a compartment separate from the water vessel, which is then connected to the heat source by a metal rod.
Heat is transferred from the heat source to the water through the metal rods, causing the water to be converted into steam. Once the steam is released from the boiler, it is collected in a steam bag above the vessel. This helps the steam condense and build up enough pressure before it leaves the system. This step is critical for industrial boilers since many industrial processes require pressurized steam when running machines.
The amount of pressure built up in the steam bag depends on the purpose of the heating. For example, driving a turbine may require a higher pressure than steam processing for agricultural soils. Industrial boilers are also equipped with safety valves to ensure that excess steam is released in the event of excessive pressure and to prevent explosions. The safety valve is usually connected to a specially installed chimney to provide a discharge path for heat as it passes through the vessel.
The burner is responsible for mixing fuel and air and igniting the mixture to produce the heat needed to bring water to a boil. It directly affects the efficiency and emissions of the boiler.
This is where the fuel is burned to produce heat. The combustion chamber must be able to withstand high temperatures and pressures, so the quality of its construction and materials is critical to safe operation.
The heat exchanger transfers the heat from the combustion gases to the water in the boiler, converting it to steam or hot water.
These tubes carry the water that is heated and eventually converted to steam.
In a water tube boiler, the steam ladle separates the steam from the water, ensuring that only dry steam leaves the boiler. This separation is essential to prevent damage to downstream equipment and processes.
A superheater raises the temperature of steam above its saturation point, thereby increasing efficiency and helping to meet the higher pressure and temperature requirements of specific industrial processes.
Coal economizers utilize the waste heat in the flue gas to preheat the feedwater entering the boiler.
Safety valves are critical to preventing overpressure situations by releasing excess steam to ensure safe boiler operation and protect equipment and personnel.
Modern industrial boilers are equipped with advanced control systems to manage various functions such as fuel supply, air flow, water level and steam pressure to ensure optimal boiler performance and safety.
The feedwater system supplies water to the boiler and usually includes components such as pumps, valves and tanks to ensure a steady flow of water supply.
Poor water quality is a potential threat to any industrial boiler. Proper water treatment prevents scaling, corrosion and contamination within the boiler system. Deaerators are used to remove oxygen and carbon dioxide from the water, while technologies such as reverse osmosis (RO) and chemical dosing remove any residual impurities before the water is fed into the boiler.
A burner mixes fuel with air and ignites it to produce high temperature combustion gases. The choice of fuel (e.g., natural gas, propane, oil, coal, or alternative fuels) affects boiler performance and emissions.
Hot gases transfer heat energy to the water circulating in the system. As the water absorbs heat, it gradually transforms into steam.
Steam may be passed through a superheater to reach higher temperatures for specific industrial applications such as turbines in power plants.
Hot gases pass through the boiler and are exhausted through the stack. These gases typically pass through the economizer, which captures the residual heat and is used to preheat incoming boiler water.
In most systems, condensate (water that condenses back to liquid form from steam) is recycled back to the boiler. This practice reduces water and energy consumption.
Steam boilers efficiently convert heat energy into electricity. First, the boiler uses heat from the combustion chamber to evaporate water into steam. Next, the steam builds up pressure and turns turbine blades, which rotate the shaft and generate mechanical energy. Finally, the rotating shaft is connected to a generator that converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. This type of power generation can be used on an individual scale to offset energy costs for industrial or manufacturing facilities, or on a large scale.
Steam boilers are widely used in the food and beverage industry. Due to the risk of cross-contamination and foodborne illness, boilers must be able to generate high-temperature water and steam for sanitary cleaning in restaurants and food production facilities. Tools, surfaces and even produce can be sanitized by steam cleaning or wiping with hot water to eliminate bacteria and foodborne pathogens.
In a beer brewery, steam boilers are also used for sanitizing, but may require more individualized control. During the brewing process, a steam boiler heats water to a specific temperature to create a flavorful beverage. Boilers in beer brewing applications require precise temperature control to achieve the perfect taste.
Steam boilers have a unique application in agriculture - soil steam sterilization. According to the Agricultural Soil Steam Sterilization Association, soil steam sterilization is a green farming technique that kills weeds, bacteria, fungi and viruses without leaving any harmful residue. The process eliminates most of the factors that can damage crops while helping to increase yields. Depending on the size of the agribusiness, a high-capacity boiler may be required.
While the pharmaceutical industry may not immediately come to mind when discussing boiler systems, steam is vital in pharmaceutical production. Steam is used for drying, sterilizing, initial cleaning, tabletting, and other manufacturing steps. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, boilers must be able to accurately control temperatures in order to purify medicines. In addition, clean or pure steam is needed to ensure that the sterilization process is free of any contaminants that could affect the final product. Clean steam comes from uncontaminated, additive-free water.
In chemical processing, steam is used to heat or cool a reactor to a specific temperature to catalyze a reaction. Depending on the type of reaction, steam output can fluctuate greatly from day to day or even hour to hour. Therefore, boilers used in this industry must be able to operate efficiently on this cycle to avoid wasting steam or fuel.
Steam is integral to the textile manufacturing process. First, there is the pretreatment stage, where hot steam is used to treat raw materials or fabrics to remove dirt and other impurities that would otherwise affect the quality of the textile. In the dyeing stage, precisely controlled steam provides just the right amount of heat and moisture for each unique fabric to optimally absorb dyes. At the finishing stage, steam removes wrinkles from the fabric so that it can be rendered in perfect condition. Large-scale steam treatment is more efficient than using traditional irons or heat alone.
Boilers provide stability and efficiency to business operations, so maintenance is a critical step in protecting your business. Keeping the entire system in good working order not only ensures smooth operations, but also employee safety.
Common maintenance measures include checking water quality, looking at smaller components such as steam management systems (or valves), and making sure all piping is in good condition. Contacting an experienced, professional plumbing company in your area to maintain your boiler system will ensure that your system doesn't break down and prevent disruptions to your operations.
If a boiler burner malfunctions, the boiler will not be able to produce heat efficiently, or at worst, at all. While industrial boilers are often designed to be robust and last for decades, burners can still occasionally fail. The burner's pump, injectors and nozzles can all cause failures, but replacing the relevant parts in a timely manner can reduce downtime.
Regardless of the fuel used in a boiler (gas, oil, coal or other alternative fuels), achieving a good mixture of fuel and air is essential for maximum efficiency. If the boiler does not burn the fuel correctly, the output will be poor and fuel will be wasted that could have been used to produce the same amount of heat with less fuel.
Any machine that operates under high pressure is prone to leaks, and boilers are no exception. For example, a leak in a tube in the combustion chamber can cause the boiler to stop working. Such leaks usually require a welded repair to bring the boiler back into operation.
Non-destructive testing is required every 5 years to look for any defects in the boiler. Any problems, such as cracks, must be dealt with as soon as they are found. The defective part can be removed and a patch plate can be welded to bring the boiler back into service.
Like domestic boilers, industrial boilers have a complex control system to ensure that they operate efficiently and within safe limits. A control panel is used to manage the burner and all other functions of the boiler, and any problems with the control system can lead to a complete shutdown. Any problems with the control system need to be diagnosed by an engineer, who may need to replace a faulty sensor, probe or valve.
There are several factors to consider when choosing an industrial boiler. Firstly, it is important to define the required output and the level of efficiency you expect to achieve. Each option has a specific investment cost.
In order to make the best decision, you also need to consider the impact of the industrial steam boiler on long-term operations. For example, how much steam does your facility currently use? What type of output is required (i.e., high pressure steam, low pressure steam, superheated steam, hot water, domestic hot water)? At what pressure and temperature should the boiler operate? What is the desired boiler efficiency? What type of fuel will be used to power the burner (i.e. natural gas, oil, propane, biofuel)? Where will the boiler be installed? Is the installation location convenient for operation and maintenance? Are local weather variations significant throughout the year (e.g., humidity, temperature, etc.)?
Industrial boilers play an important role in a variety of fields as the core equipment of many industries, with their diverse types and complex operating principles. From power generation to food processing, from agriculture to pharmaceuticals, industrial boilers are everywhere. Understanding its working mechanism, main components, common problems and maintenance points, to ensure efficient and safe operation of enterprises is essential. When choosing an industrial boiler, a combination of factors can ensure that you find the most suitable solution for your organization. We hope this article will help you better understand industrial boiler systems, and prompt you to rationalize boiler maintenance or evaluate new boiler options based on the actual situation.